High-level Workflow
Reverse Verification Flow
In the case of Nitro, under the reverse verification flow, we use permissionless entities called forwarders to transfer tokens. Once a cross-chain token transfer request is initiated by the user on the source chain Nitro contract, a forwarder will pick up the event corresponding to the request and provide the user with that token on the desired destination chain. At a later time, the forwarder can claim the user-deposited token from chain A. Step-by-step flow for the entire process is given below:
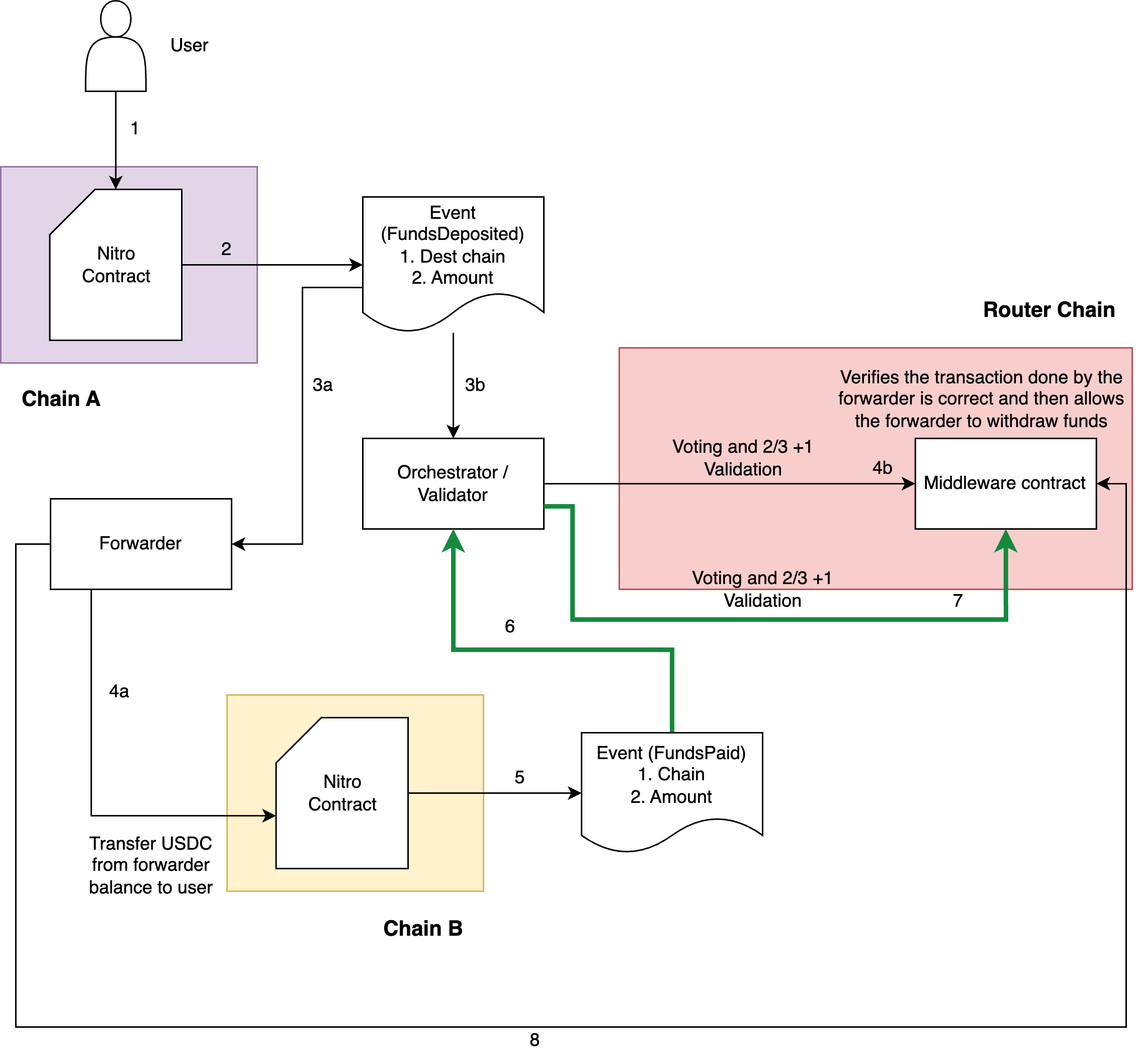
Step 1) User invokes the Nitro contract to transfer funds from Chain A (source) to Chain B (destination).
Step 2) The Nitro contract will validate the request, deduct funds from the user's account, increment event nonce and emit a CrosschainTransferRequest event. The event includes the following details:
SrcChainIdEventNonceDestChainIdReceiverAddressTokenAmount
Step 3a) A forwarder will listen to the CrosschainTransferRequest event
Step 3b) Orchestrators on the Router Chain will also listen to the CrosschainTransferRequest event and submit it to the Router Chain with their attestation.
Step 4) The forwarder will create a hash of the fields included in the event and submit a transaction to the destination chain Nitro contract. The hash acts as a unique identifier for the CrosschainTransferRequest.
Step 4b) After 2/3+1 validation, the Router Chain will invoke the middleware Nitro contract with the event info. Upon receiving the CrosschainTransferRequest event, the middleware contract will persist the request (mapping to the request will be maintained using the hash of the fields included in the event).
Step 5) Upon receiving the tx, the Nitro contract on the destination chain will (a) transfer the defined amount from the forwarder address to the receiver address; (b) persist the hash in the status map (to skip the replays); (c) emit a CrosschainTransferExecuted event confirming the execution. The event includes:
ChainIdEventNoncehashForwarderAddress
Step 6) Orchestrators on the Router Chain listen to the CrosschainTransferExecuted event from the destination chain Nitro contract and submit it to the Router Chain with their attestation.
Step 7) Upon 2/3+1 validation, the Router Chain will invoke the middleware Nitro contract with the event info. Upon receiving the CrosschainTransferExecuted event, the middleware contract will mark the request as Completed and persist the Forwarder address and amount.
Step 8) Once the request is marked as completed, the forwarder can claim its (funds + reward) by triggering an outbound request. The outbound request gets processed via the Router Chain and existing Gateway contracts. The Gateway contract will invoke the source chain Nitro contract, which will settle the funds for forwarder.
Burn and Mint Flow
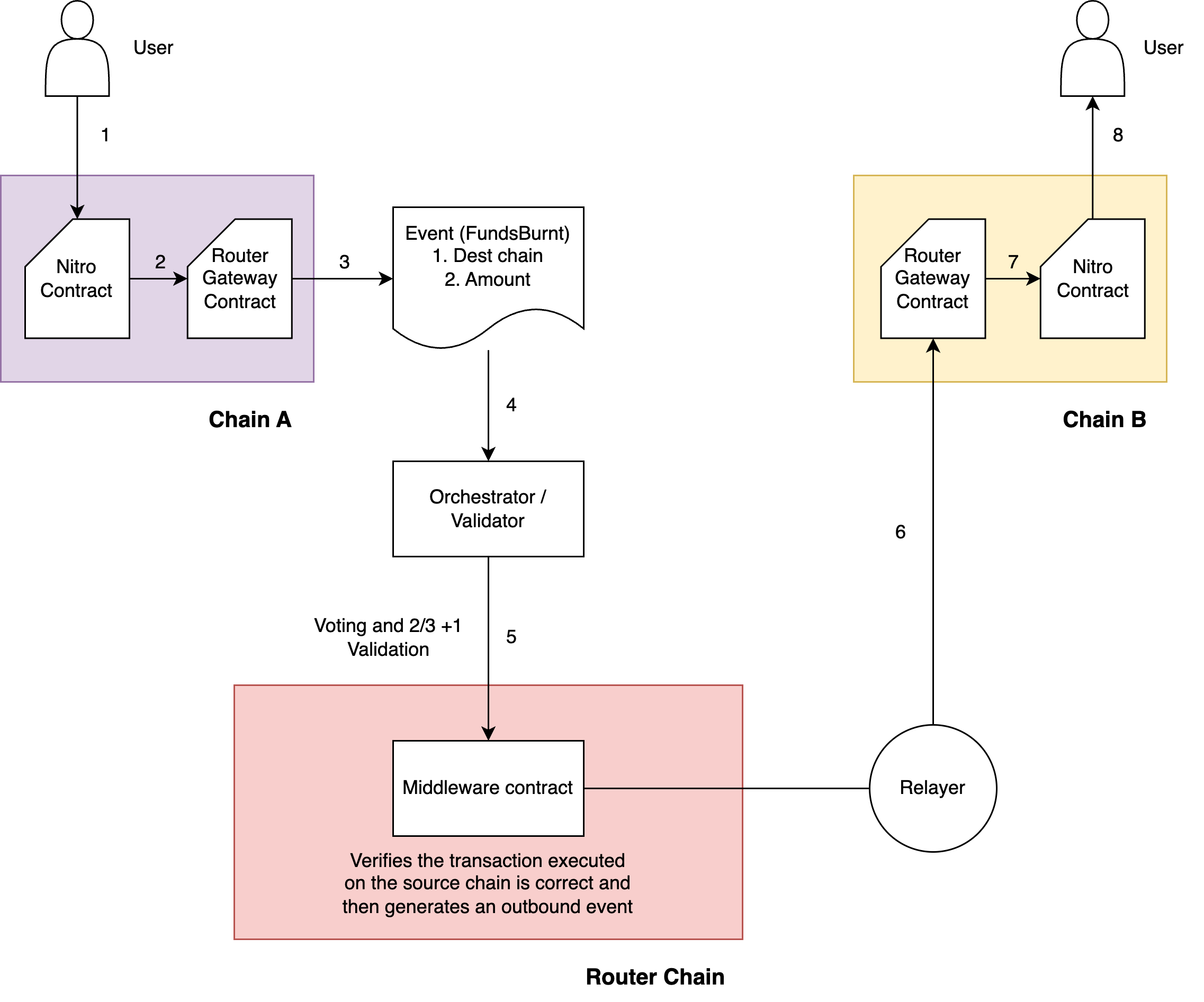
Step 1) User invokes the Nitro contract to transfer funds from Chain A (source) to Chain B (destination).
Step 2) The Nitro contract will validate the request, deduct funds from the user's account, burn them, and invoke the iSend() function on the Router Gateway contract.
Step 3) The Gateway contract on the source chain emits an event that is listened to by the orchestrators on the Router Chain.
Step 4) Orchestrators on the Router Chain will listen to the CrosschainRequest event and submit it to the Router Chain with their attestation.
Step 5) After 2/3+1 validation, the Router Chain will invoke the middleware Nitro contract with the event info. Upon receiving the CrosschainRequest event, the middleware contract will validate the request, generate an outgoing request from the Router Chain to the destination chain, and pay the fees associated with the outgoing request.
Step 6) Once the outbound request initiated by the Nitro bridge contract is validated by the orchestrators, a Nitro relayer picks it up and forwards the event to the Router Gateway contract on the destination chain.
Step 7) Upon receiving the request from the relayer, the Gateway contract on the destination chain will invoke the Nitro contract.
Step 8) The Nitro contract will parse the message payload and mint the tokens to the user’s address on the destination chain.
Note: This flow does not make use of the forwarders; therefore it is necessary to validate the request before it is executed on the destination.