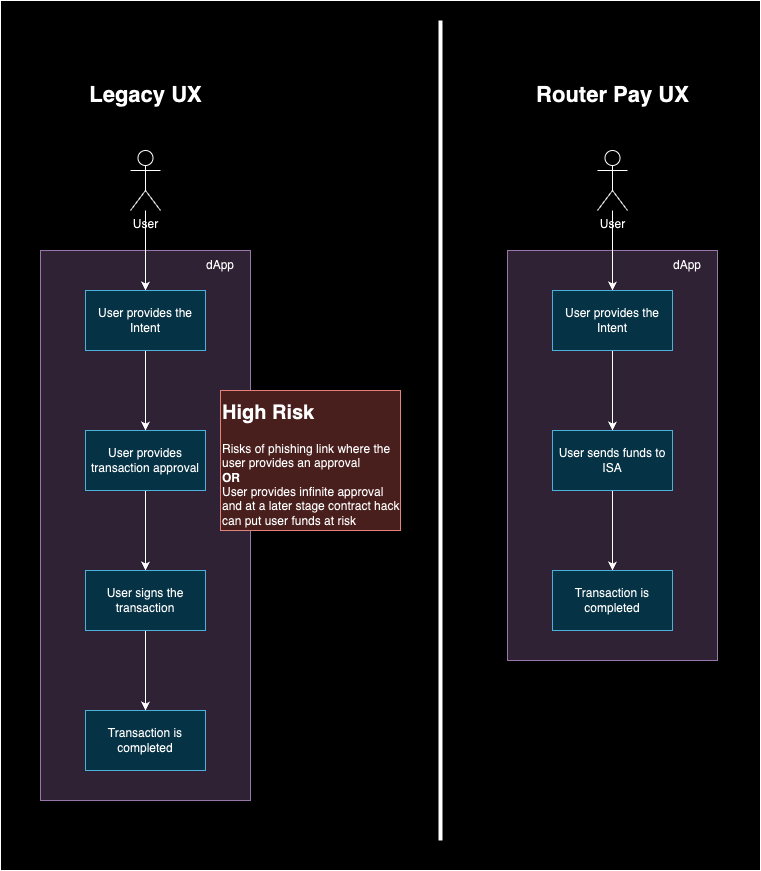
User Journey with Router Pay
Router Pay simplifies the workflow for end users and reduces the risks of approvals and phishing websites from their dApp interaction journey. Below we have shown the difference in the journey for a user in the legacy dApps vs the ones which use Router Pay.
How does Router Pay work?
Interaction Setup
- User begins by selecting a desired DApp interaction, such as a cross-chain transfer or interaction with a decentralized application.
- User inputs key parameters for the interaction, including:
- Target Address (callTo): Where the assets will be sent or utilized. This will be the dApp contract address.
- Approval Address (approvalTo): The address authorized to handle token transfers (if required).
- Encoded Data (data): Details about the transaction.
- Source Token (srcToken): The asset type for the interaction.
- Refund Address (refundAddress): Address to receive refunded assets if the interaction fails.
- Expiry Time: The maximum time allowed for the transaction to be completed.
QR Code Generation
- RouterRelay Contract generates a unique deposit address using the provided parameters, and this address can be encoded as a QR code for easy user access.
- The User can simply scan the QR code, aligning with a familiar Web 2.0 experience.
Asset Transfer
- User transfers assets (tokens or native assets) to the generated deposit address.
- DepositReceiver Contract is deployed at this address to hold the assets temporarily.
Execution and Forwarding
- ReceiverImplementation.receiveAndSendToken is called via delegatecall by DepositReceiver, attempting to forward the assets to the specified callTo address.
- Conditional Solver Check:
- If assets are successfully forwarded to the specified address within the expiry time:
- The Solver validates the transaction parameters, including balance and expiry time.
- Upon successful validation, the Solver triggers the final transaction, completing the interaction on behalf of the user (e.g., cross-chain transfer).
- If conditions aren’t met or the expiry time is reached without adequate balance, assets are automatically refunded.
Refund Mechanism (if applicable)
- If the transaction forwarding fails or the expiry time is reached without triggering, the following occurs:
- DepositReceiver sends the remaining balance to the refundAddress, ensuring user funds are secure.
- DepositReceiver then self-destructs to free resources, ensuring that temporary contract storage is cleared.
Completion
- If successful, the transaction completes as intended, with assets transferred to the DApp or cross-chain destination.
- User receives confirmation of the transaction status and any relevant details about the final destination of their assets.