Orchestrators
Router orchestrators are entities that listen to incoming cross-chain requests from other chains, attest their validity, parse them into a unified format and post them on the Router Chain. These attested requests can then be picked up by the relayers and forwarded to the destination chain. All validators must run an orchestrator instance to be a part of the Router Chain ecosystem.
Working of an Orchestrator
At a high level, a Router orchestrator works like a funnel that gathers events from various chains and posts them to the Router Chain. To do so, an orchestrator uses a listener and dispatcher model wherein the listener module aggregates events while the dispatcher module forwards these events to the Router Chain.
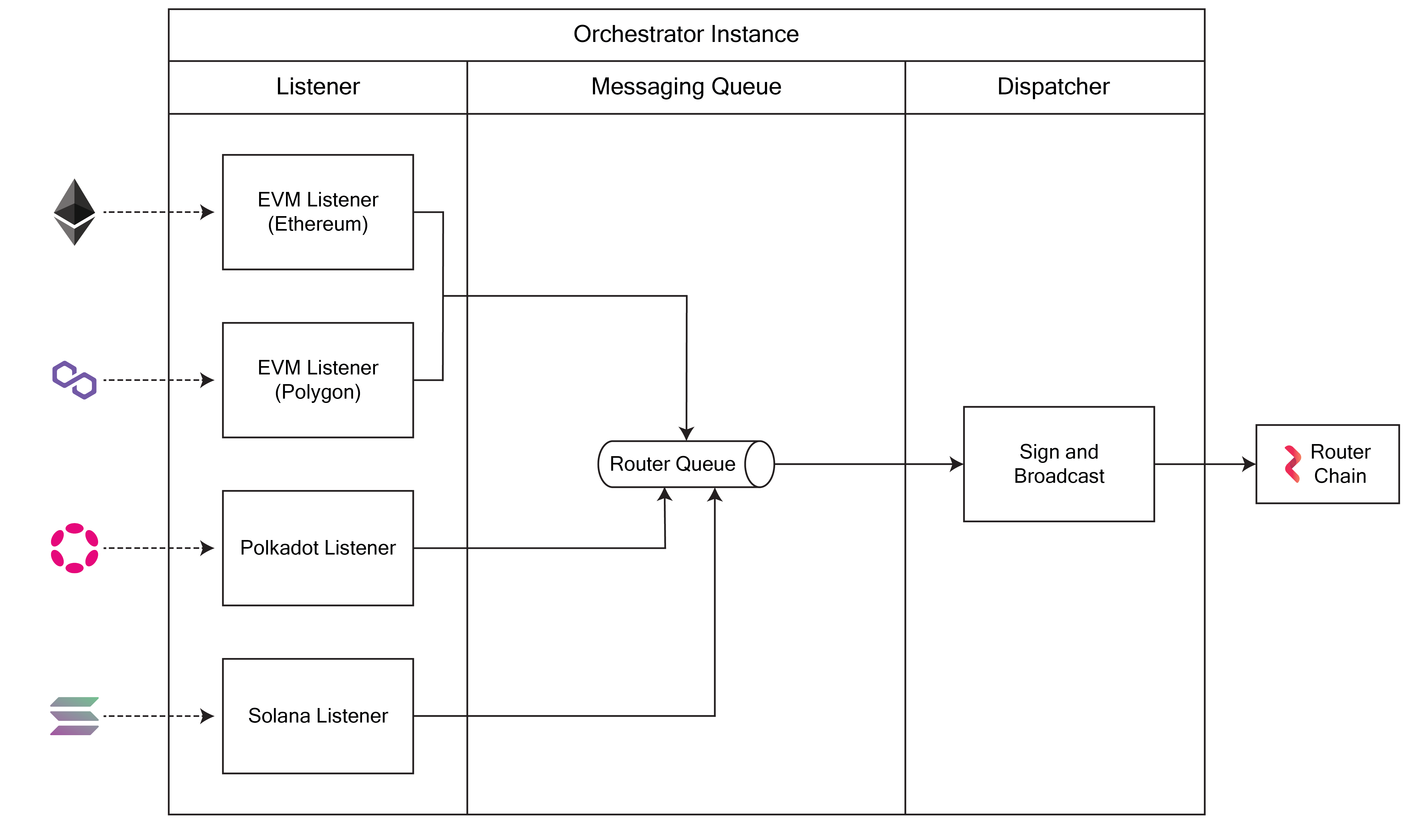
- Listener: The listener module of an orchestrator listens to events emitted from specific chains based on the
chainTypeparameter in the configuration provided to it. Listeners operate as threads (goroutines) under an orchestrator. All listeners subscribe to multiple types of events - a regular iSend (cross-chain send) event, an iRecieve (cross-chain receive) event, and an iAck (acknowledgment) event for gateway contract. Once the listener module receives an event, it waits for the preconfigured amount of network confirmations (for example, 10 network confirmations for requests originating from Mumbai/Fuji) before parsing it into a message. After receiving event, it transform message according to router chain, once the message is prepared, the listener adds it to a transaction queue sequence database. - Attester: For request originting from router chain, it is required to submit the attestation for the transaction. Attester module, will query chain to get such transaction check for the attestation, if not present, it attest the transaction and add to no sequence database queue.
- DB Queue: The queue is used to store and deliver transformed messages to consumers (dispatchers) in a first-in-first-out manner while ensuring that duplicate messages are being ignored.
- sequence DB: Request present in this DB should processed sequentially (sorted by nonce).
- no sequence DB: Request present in this DB can be process in any sequence.
- Dispatcher: The dispatcher module is essentially responsible for streamlining the incoming requests by (a) listening to the queue, (b) batching the transaction (c) signing the messages, and (d) broadcasting them to the Router Chain.